
Indiana Dog Bite Law: What You Need To Know

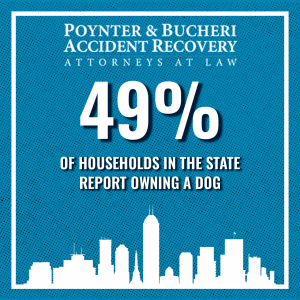
Nearly half of Indiana households own at least one dog. Although these pets make great companions, they’re still animals, and no amount of training can remove their territorial instincts and defensive behaviors. Even expertly-trained dogs can bite adults and children, causing injuries ranging from minor to fatal.
If you were bitten or attacked by a dog, you might suffer from injuries that require expensive medical treatments, which may also impact your mental and emotional well-being. Fortunately, you can file a claim or lawsuit against the dog’s owner after an attack, but you may struggle to recover compensation in some situations.
Dog bite laws differ from state to state, so if you or a loved one was attacked, it’s important to know about Indiana dog bite laws and how they will impact your ability to recover damages. Here’s what you need to know.
Indiana’s One-Bite Law

Like many states, Indiana uses what’s known as the “one-bite rule,” meaning that if a dog has never shown signs of aggression before biting a victim, the pet owner may not be liable for damages. However, suppose the dog has already bitten or attacked someone previously. In that case, the dog’s owner will usually be responsible for the damages that the pet causes, assuming that the victim wasn’t trespassing on the owner’s property.
Unfortunately, it’s often tricky to tell whether or not a dog displays what could be considered “aggressive behavior,” but some signs that a dog may eventually harm someone include:
- Snapping at someone even if they don’t make contact
- Aggressive barking or growling at humans
- Purposely running into a human with enough force to knock them over
- Attacking or fighting other animals
Another important note is that some areas of Indiana restrict or regulate certain dog breeds that purportedly have propensities for aggression. This can also impact whether or not the one-bite law will apply. For example, Fowler County and Kirklin County have banned pit bulls. Here’s a complete list of breed restrictions and ordinances in our state.
Situations Where the One-Bite Law Doesn’t Apply
Despite Indiana’s one-bite law, there are still many situations under Indiana’s dog bite law in which a dog owner may be responsible for damages, even if their pet has never shown signs of aggression.
Indiana Code § 15-20-1-3 states that if a dog bites a government employee while they are carrying out their duty, the owner will be liable regardless if their dog has ever shown signs of aggression. This detail protects postal workers, police officers, and other government employees who may be susceptible to dog attacks.
Additionally, if the dog owner acted negligently at the time of the bite, a victim may still be able to recover compensation even if the dog didn’t show signs of aggression previously. For example, if a dog charged at a person without provocation and the owner made no attempt to restrain the animal, the pet owner acted negligently. The pet owner may also be liable if a dog attacks a person on someone else’s property.
If a dog owner displays gross negligence or willfully had their dog harm someone, they could be held criminally liable for their dog’s behavior. They could face a Class C misdemeanor, which comes with a fine of up to $500 dollars and 60 days in jail. In the event that a victim suffers fatal injuries after a dog attack, the pet owner could face felony charges.
Is the Owner Always At Fault After a Dog Bite?
Although pet owners are often exclusively liable when their dogs attack, there are situations in which the victim may be partially liable, impacting their ability to recover damages. These situations include:
- Intentionally interacting with an aggressive dog: If the victim was aware of the dog’s aggressive tendencies but still insisted on interacting with it anyways, they may be considered partially responsible for their own ensuing injuries.
- Not exercising reasonable care when interacting with the dog: In the event that the victim was reckless when approaching the animal, such as charging at it or engaging in another provoking behavior, they may be partially or fully responsible for their own injuries.
- Not following warnings: Have you ever seen a “Warning: Beware of Dog” sign? If a victim chooses to ignore these signs, they may be considered partially responsible. Additionally, if the dog displayed aggressive warning signs, like growling, yet the victim attempted to pet the animal anyways, they could be considered partially liable.
Even if a victim is partially liable, they can still recover compensation as long as they’re considered less than 51% responsible, but their percentage of responsibility will directly impact their compensation. For example, let’s say you chose to pet a dog after it growled at you, resulting in it biting you. After reporting the dog bite, the authorities could assign you a percentage of responsibility for your own injuries. If they deem you 20% responsible, that will reduce your total compensation by 20%.
Contact an Indiana Dog Bite Lawyer
Indiana dog bite law can get complicated quickly, and if you were injured by one of these animals, you need to do everything you can to recover compensation for your injuries. You can significantly increase your chances of receiving the full damages you deserve by contacting an Indiana dog bite lawyer.
Fortunately, you can contact Poynter & Bucheri Accident Recovery Attorneys at Law to maximize the amount of compensation you can recover. Depending on your case, you may receive damages for medical bills, lost wages, loss of future earnings, pain and suffering, and more.
Get a FREE case review today by calling 1-800-265-9881, or you can contact us online here.
